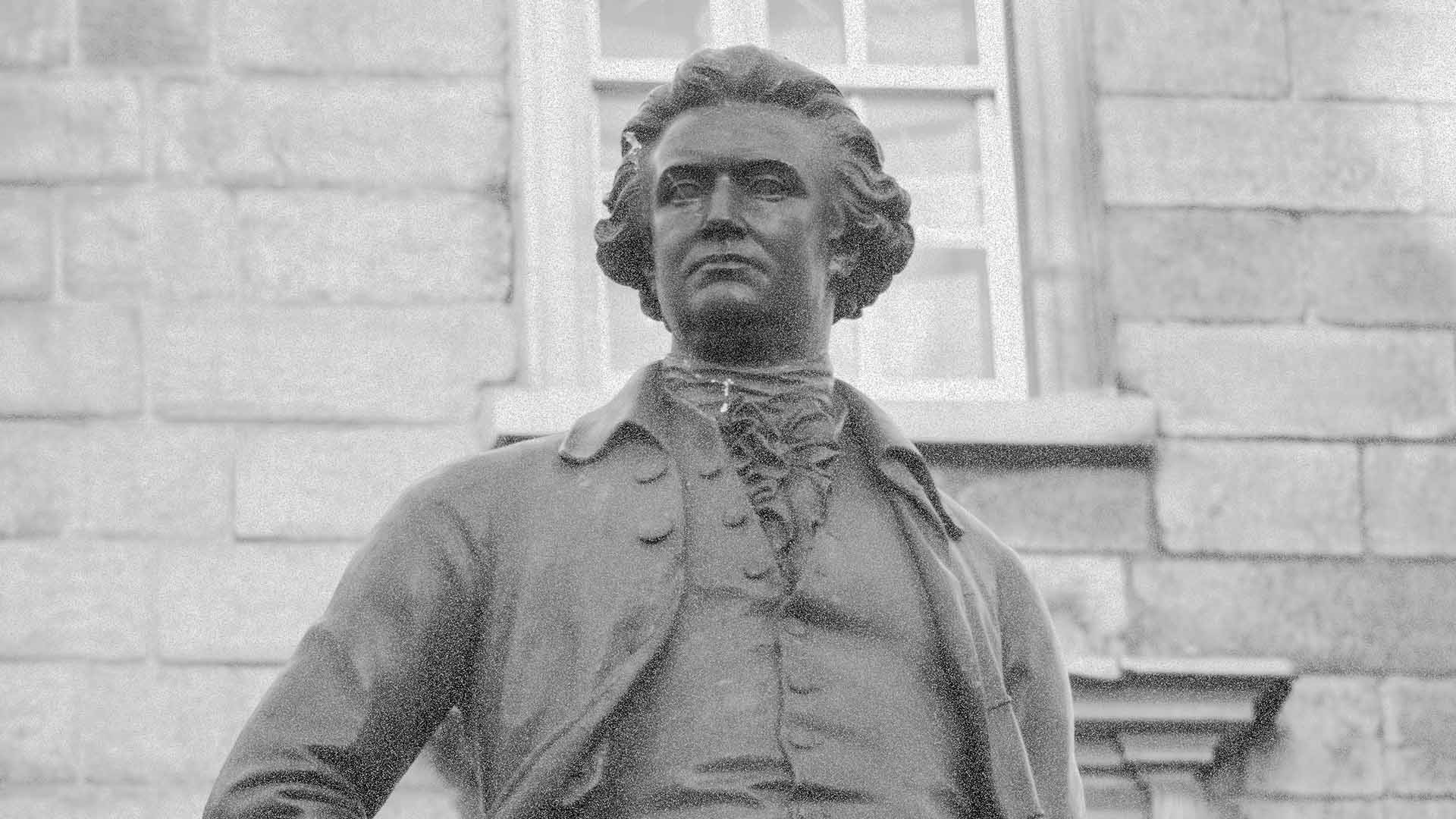Edmund Burke Statue

Edmund Burke Statue
Edmund Burke Statue, Edmund Burke 1729-1797 Irish Statesman served in the Whig Party in House of Commons.
Edmund Burke Statue, Edmund Burke 1729-1797 Irish Statesman served in the Whig Party in House of Commons.
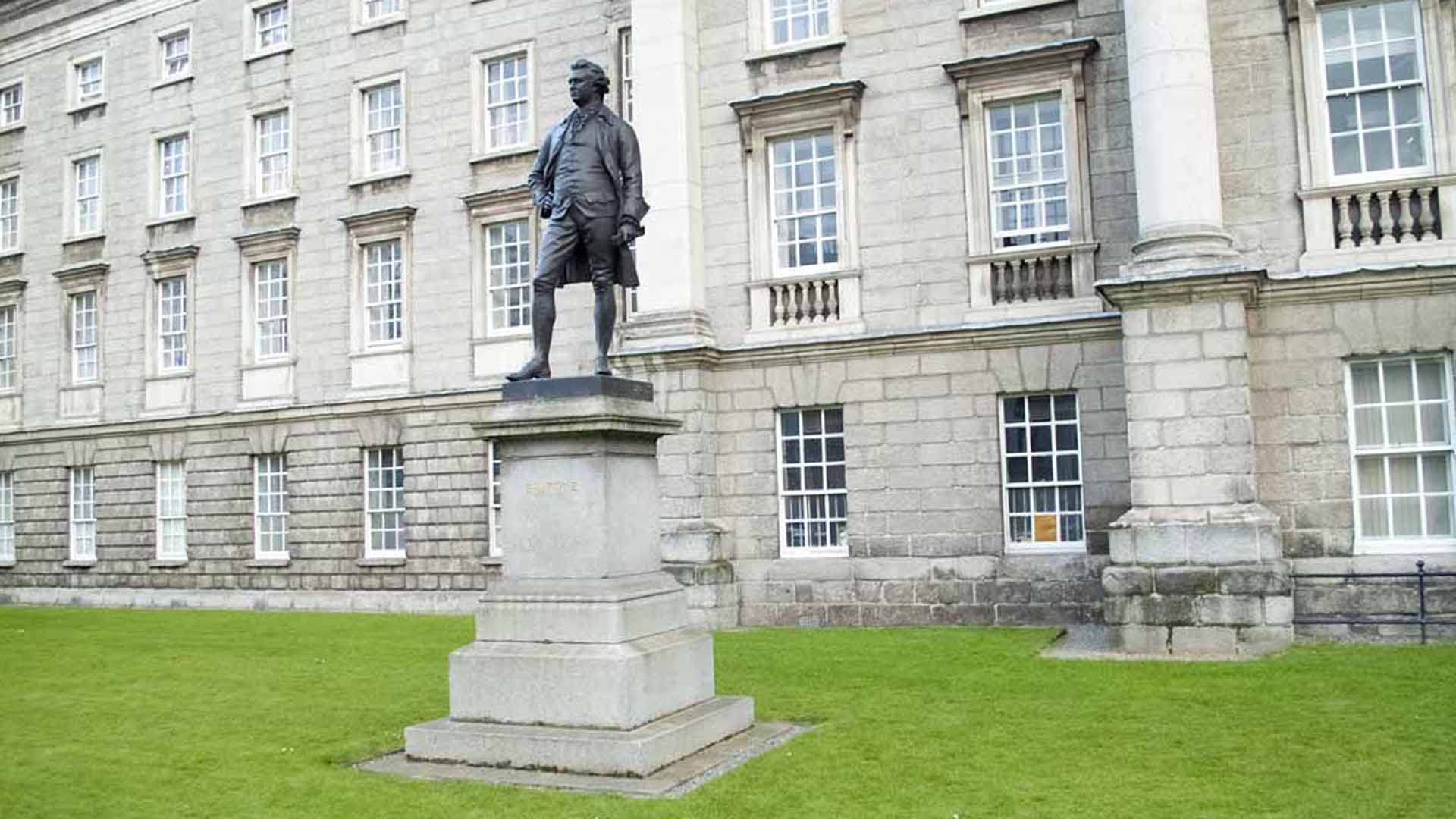
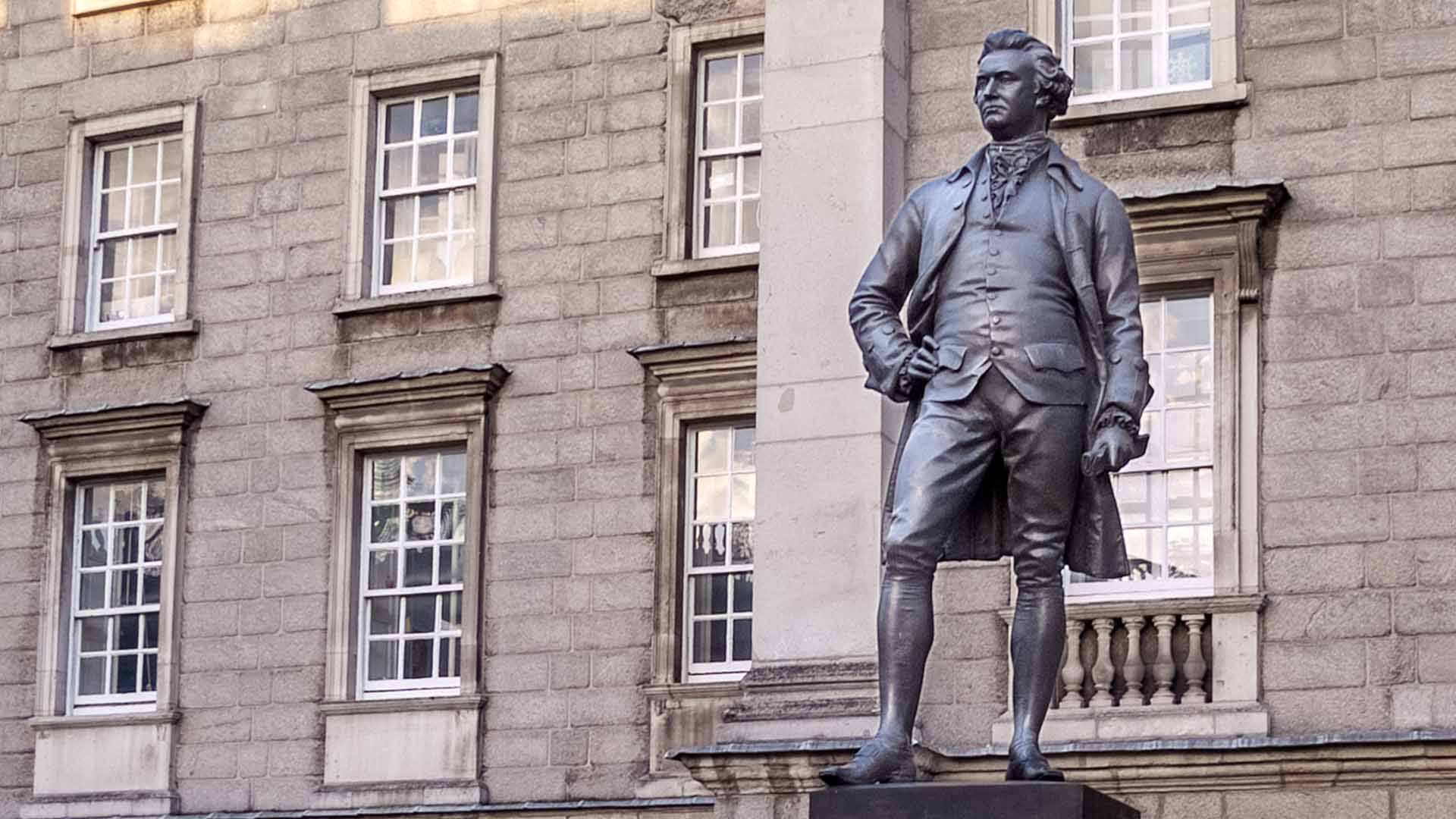
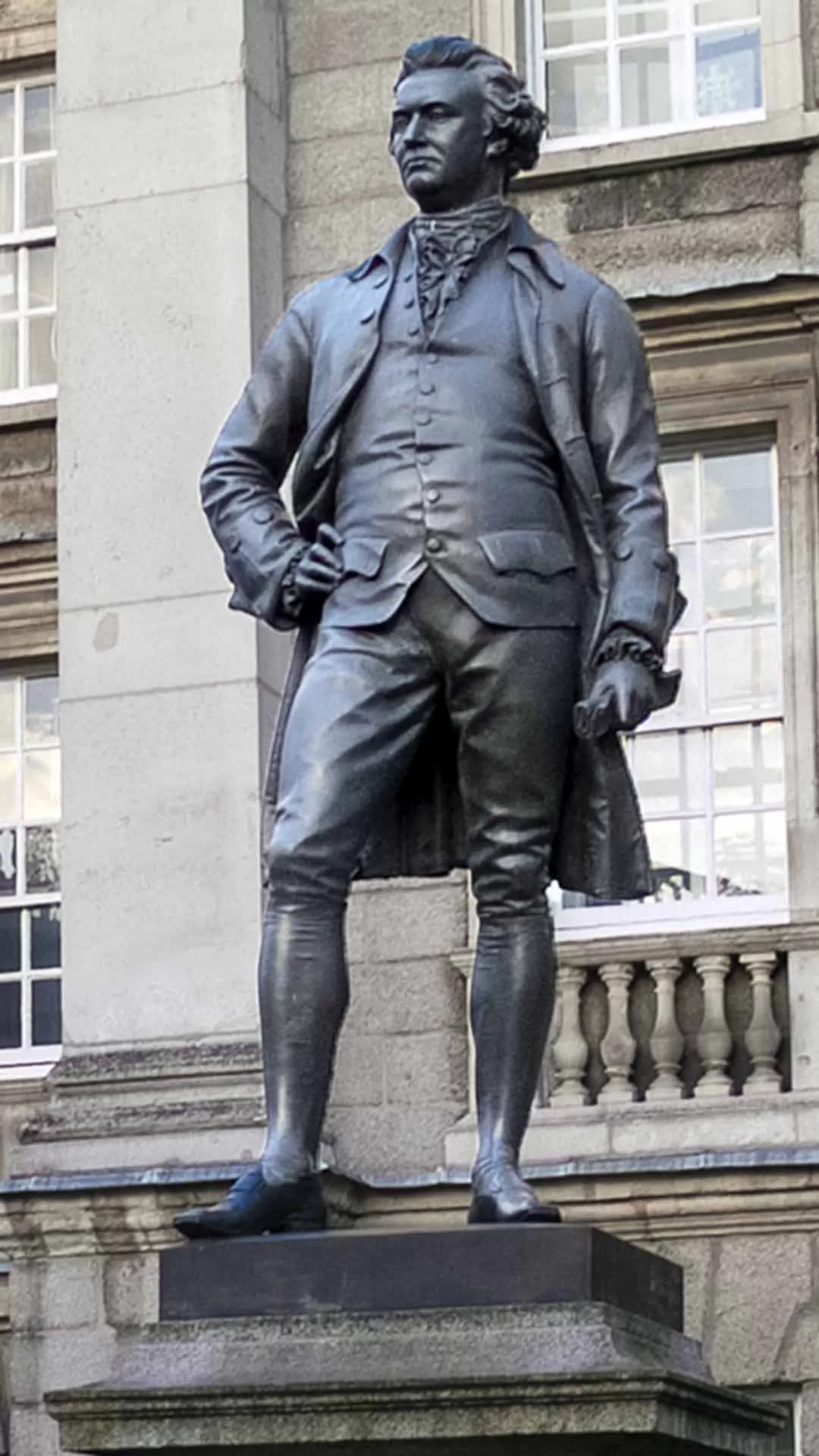
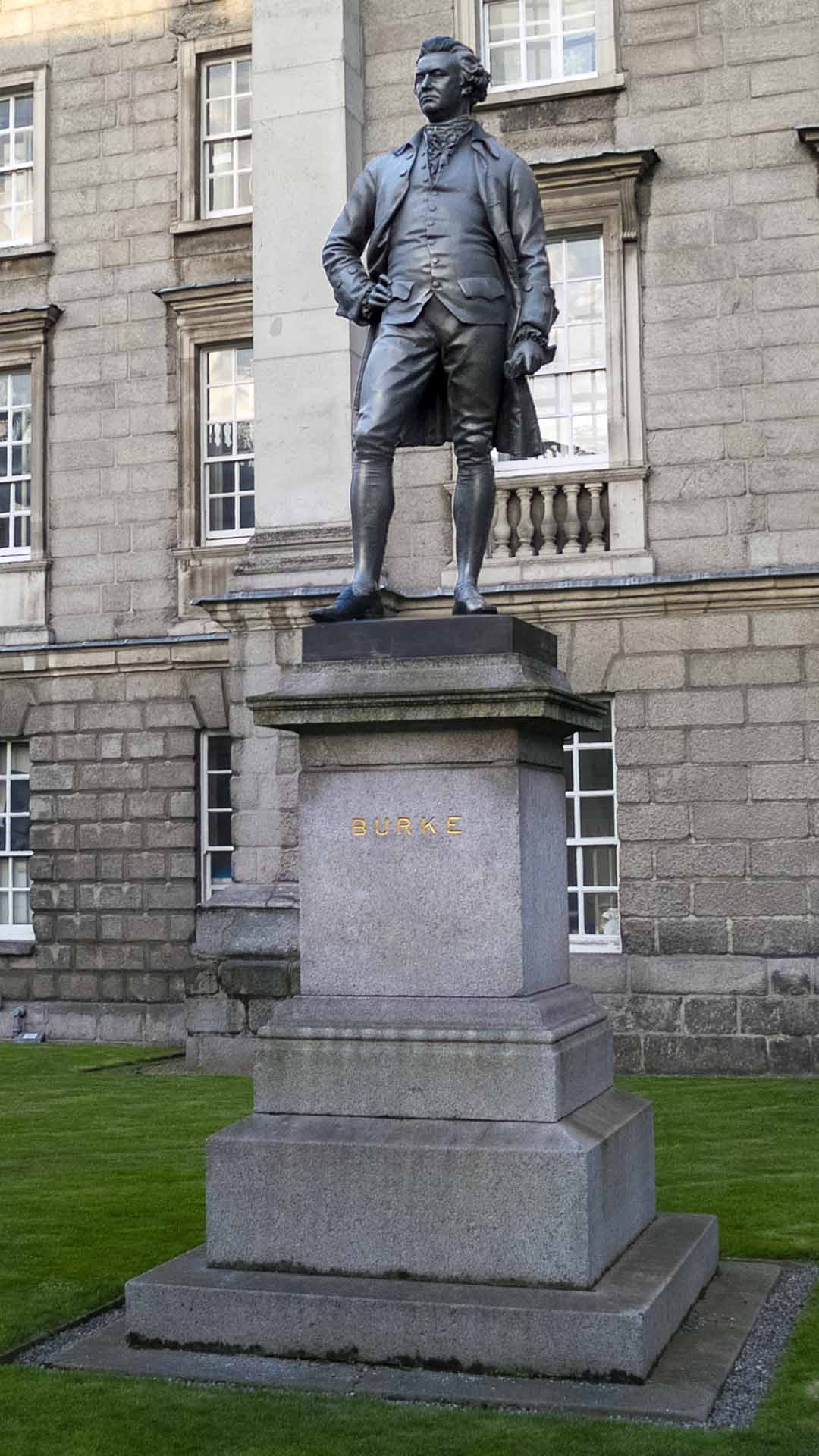
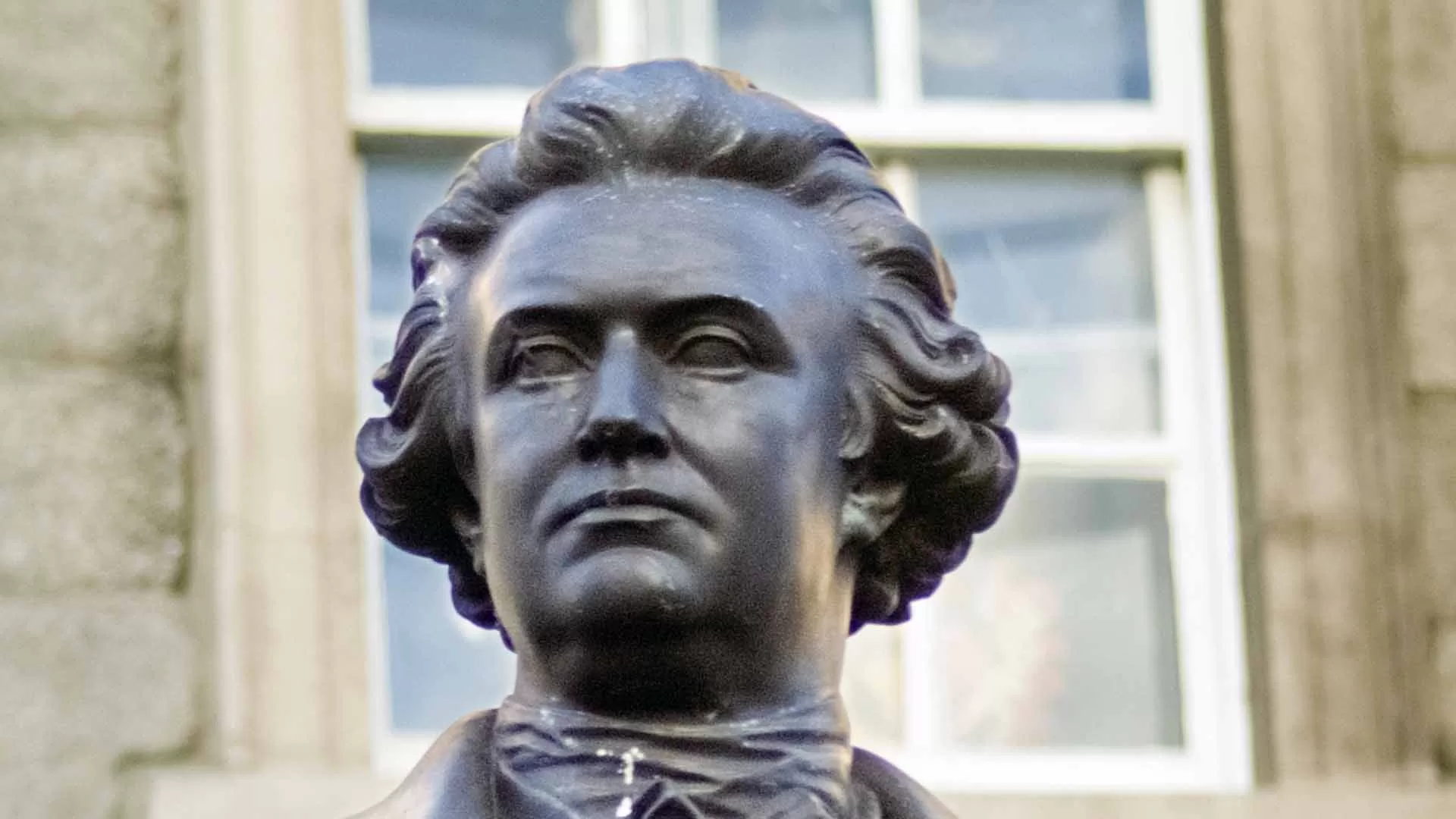
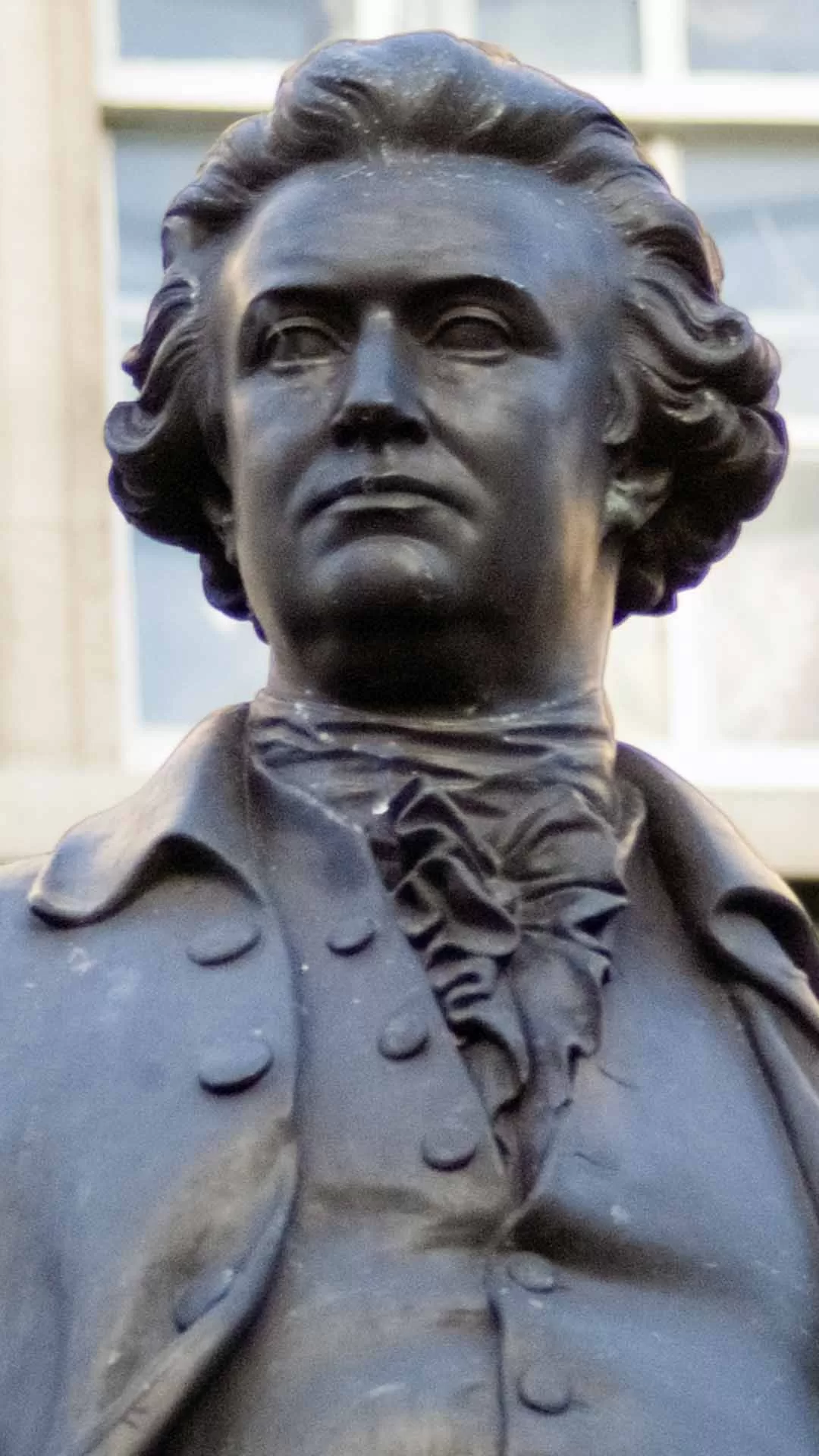






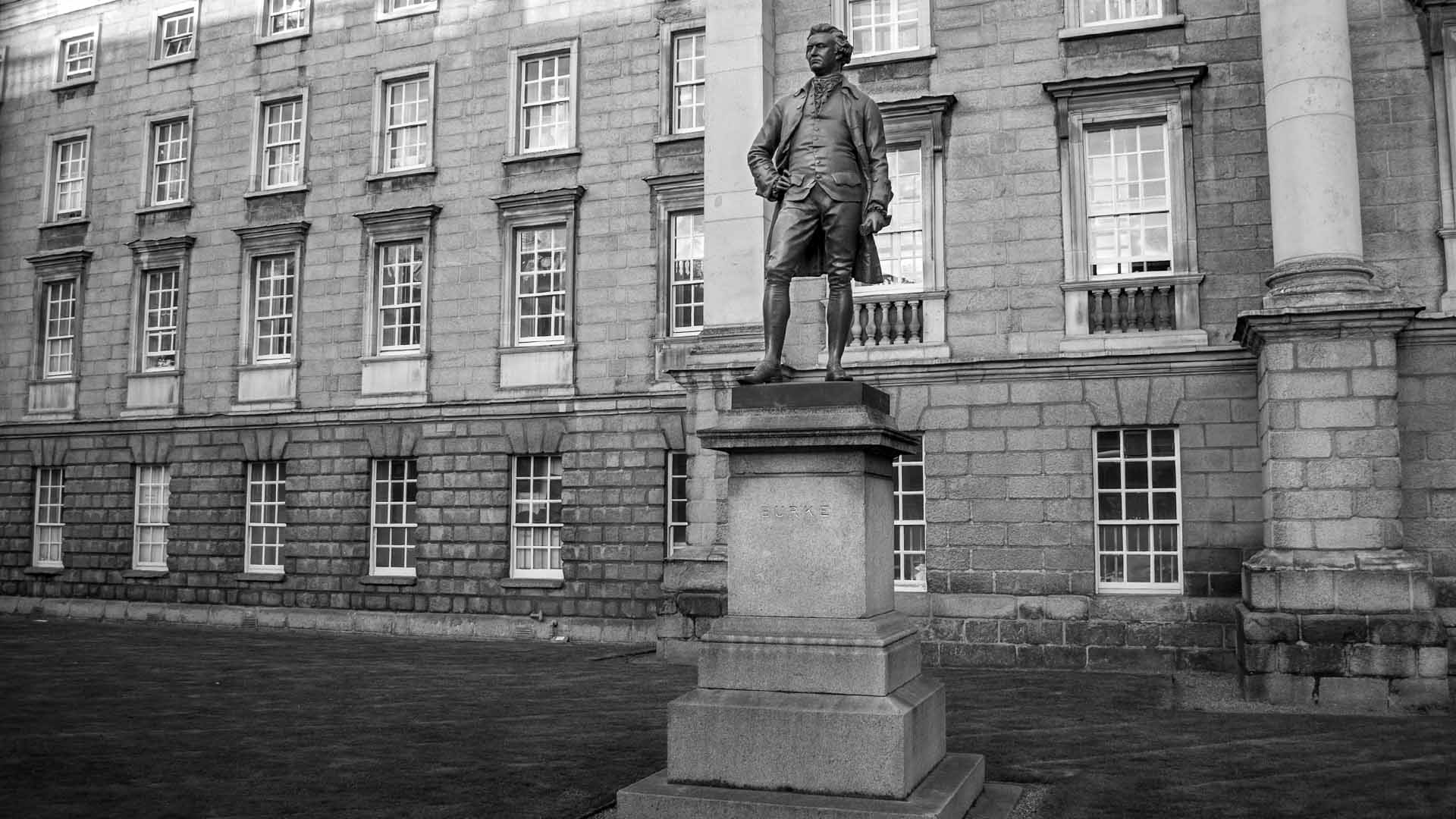
This statue was erected 1868 and unveiled by the Prince of Wales. The bronze statue was made by J.H.Foley, who had the ability to capture his subjects by their stance. This statue of Burke is one of three created by Foley in close proximity, the other two are Goldsmith and Grattan.
This statue was erected 1868 and unveiled by the Prince of Wales. The bronze statue was made by J.H.Foley, who had the ability to capture his subjects by their stance. This statue of Burke is one of three created by Foley in close proximity, the other two are Goldsmith and Grattan.
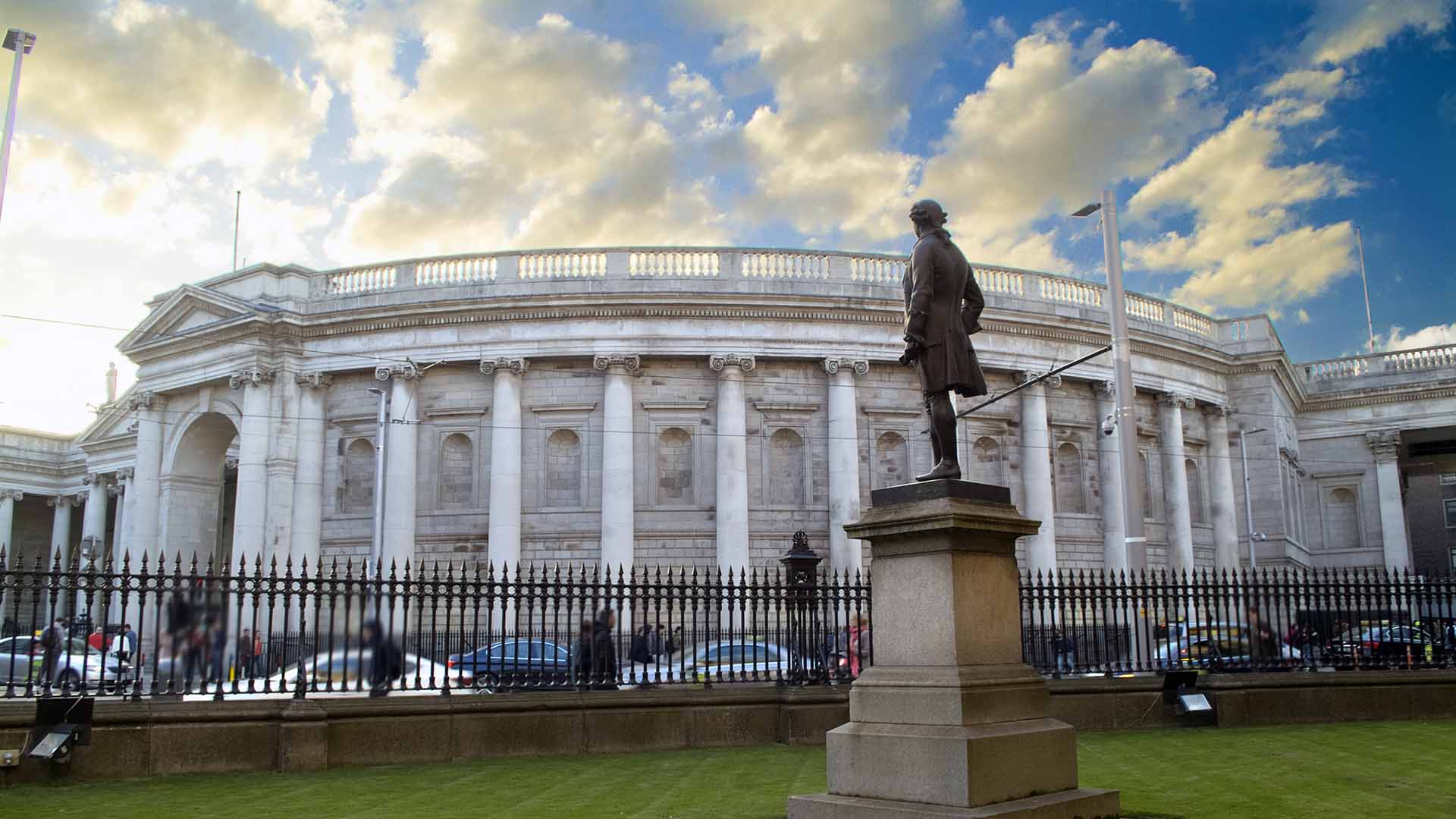


Edmund Burke keeps watch on the Bank of Ireland from Trinity College.
Edmund Burke keeps watch on the Bank of Ireland from Trinity College.
ChatGPT
Edmund Burke (1729–1797) was an Irish statesman, philosopher, and political theorist who is often regarded as one of the founding figures of modern conservatism. Born in Dublin, Ireland, Burke had a distinguished career as a politician, serving in the British Parliament and becoming a prominent intellectual figure of his time.
Key aspects of Edmund Burke’s life and contributions include:
- Early Life and Education:
- Burke was born on January 12, 1729, into a Protestant family in Dublin. He attended Trinity College, Dublin, where he studied law. His early education and experiences in Ireland had a profound impact on his political and philosophical views.
- Political Career:
- Burke entered politics and, in 1765, became a Member of Parliament (MP) for Wendover. His eloquence and intellectual prowess quickly gained him recognition. Over the years, he held various positions, including serving as a member of the Rockingham Whigs and later as a member of the conservative faction.
- Philosophical Contributions:
- Burke is best known for his philosophical works, particularly “Reflections on the Revolution in France” (1790). In this seminal text, he criticized the radical changes of the French Revolution and expressed his support for gradual reform and the preservation of established institutions. His writings emphasized the importance of tradition, social order, and the complexities of human nature.
- Opposition to the French Revolution:
- Burke’s most famous work, “Reflections on the Revolution in France,” criticized the revolutionary ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity. He argued that abrupt and radical changes to established institutions could lead to chaos and the loss of individual freedoms. While his views were controversial, they influenced conservative thought and continue to be studied in political philosophy.
- Critique of Imperialism:
- Burke was also known for his opposition to British colonial policies in India, particularly his criticism of the East India Company’s governance. He advocated for justice and compassion in the treatment of colonial subjects, earning him a reputation as an advocate for human rights.
- Legacy:
- Edmund Burke’s ideas have had a lasting impact on political thought, particularly in the realm of conservatism. His emphasis on the importance of tradition, skepticism toward radical change, and respect for the organic development of society continue to influence conservative thinkers today.
- Death and Recognition:
- Burke passed away on July 9, 1797, in Beaconsfield, England. Although he faced criticism and opposition during his lifetime, his ideas gained prominence in the 19th century and beyond. Many consider him a key figure in the development of conservative political thought.
Edmund Burke’s legacy extends beyond his political career, and his writings remain an essential part of the intellectual history of political philosophy.
ChatGPT
Edmund Burke (1729–1797) was an Irish statesman, philosopher, and political theorist who is often regarded as one of the founding figures of modern conservatism. Born in Dublin, Ireland, Burke had a distinguished career as a politician, serving in the British Parliament and becoming a prominent intellectual figure of his time.
Key aspects of Edmund Burke’s life and contributions include:
- Early Life and Education:
- Burke was born on January 12, 1729, into a Protestant family in Dublin. He attended Trinity College, Dublin, where he studied law. His early education and experiences in Ireland had a profound impact on his political and philosophical views.
- Political Career:
- Burke entered politics and, in 1765, became a Member of Parliament (MP) for Wendover. His eloquence and intellectual prowess quickly gained him recognition. Over the years, he held various positions, including serving as a member of the Rockingham Whigs and later as a member of the conservative faction.
- Philosophical Contributions:
- Burke is best known for his philosophical works, particularly “Reflections on the Revolution in France” (1790). In this seminal text, he criticized the radical changes of the French Revolution and expressed his support for gradual reform and the preservation of established institutions. His writings emphasized the importance of tradition, social order, and the complexities of human nature.
- Opposition to the French Revolution:
- Burke’s most famous work, “Reflections on the Revolution in France,” criticized the revolutionary ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity. He argued that abrupt and radical changes to established institutions could lead to chaos and the loss of individual freedoms. While his views were controversial, they influenced conservative thought and continue to be studied in political philosophy.
- Critique of Imperialism:
- Burke was also known for his opposition to British colonial policies in India, particularly his criticism of the East India Company’s governance. He advocated for justice and compassion in the treatment of colonial subjects, earning him a reputation as an advocate for human rights.
- Legacy:
- Edmund Burke’s ideas have had a lasting impact on political thought, particularly in the realm of conservatism. His emphasis on the importance of tradition, skepticism toward radical change, and respect for the organic development of society continue to influence conservative thinkers today.
- Death and Recognition:
- Burke passed away on July 9, 1797, in Beaconsfield, England. Although he faced criticism and opposition during his lifetime, his ideas gained prominence in the 19th century and beyond. Many consider him a key figure in the development of conservative political thought.
Edmund Burke’s legacy extends beyond his political career, and his writings remain an essential part of the intellectual history of political philosophy.


Phil Lynott Statue


Luke Statue